HTML is the markup language used on the web, and it is used to make most of the pages you see online. But what is HTML, really?
In this article, Designveloper will give the most in-depth introduction to basic HTML that we can. Before we start, try not to get too scared. This guide is for anyone and everyone, no matter how much technical knowledge they have.
Are you ready to start getting acquainted with HTML? Let’s go.
What Is HTML?
HTML, or hypertext markup language, is a fundamental computer language that is used for the creation of websites. The knowledge of this language is an absolute must if you are thinking about pursuing a career in online design or development; nevertheless, even in other fields, such as digital marketing, even a basic understanding of HTML can be useful.
Markup languages like HTML are used to describe how your work is put together. HTML is made up of different parts called “elements”. You can use these elements to “wrap” different parts of the content to make it look or act in a certain way. With the surrounding tags, you can make text italic, change the size of the font, turn a word or image into a link to another page, and do a lot of other things to format it.
HTML is considered to be one of the three most important tools for building websites.
- HTML tells you how a website is put together, including how text, images, and other media will be shown on the page.
- Cascading style sheets, or CSS, decide how these elements look, including their colors, layout, and format.
- JavaScript makes it so that these elements respond in certain ways to what a user does.
Recommended reading: Designers Should Know How to Code?
The History Of HTML

As was already said, HTML is a type of programming language that is used to make websites. Its full name is “Hypertext Markup Language,” but people usually just call it “HTML”. HTML is a markup language that tells an internet browser how to display a document.
Tim Berners-Lee was a scientist who worked as a contractor at CERN. In the late 1980s, he came up with the idea for a system that CERN researchers would use. In a document he wrote in 1989, he suggested a hypertext system based on the internet.
As a result, HTML was made by Tim Berners-Lee, who is well known for this. Tim’s idea for a document called “HTML Tags” in late 1991 was the first time that HTML was explained to the public. Consequently, HTML5 is the most recent version of HTML, and we’ll learn more about it in the next section.
The Many Different Versions
Since HTML was first made, many different versions of it have been put on the market. The following gives a quick overview of each of these versions:
HTML 1.0: The first version of HTML came out in 1991. It was called the “barebones” version of HTML. The first version of HTML was also HTML 1.0.
HTML 2.0: This version came out in 1995. After it was first used, it became the standard language version for making websites. HTML 2.0 could add features like form-based file uploads and form parts like text boxes, choice buttons, and so on.
HTML 3.2: The HTML 3.2 version was released by the W3C at the beginning of 1997. This version added more options for form elements and made it possible to make tables. This version also had the ability to build tables. It can also host a website with complicated mathematical formulas on it. It wasn’t considered an official standard for any browser until January 1997. Even now, support for it can be found in a large number of browsers.
HTML 4.01: HTML 4.01 came out in December 1999 and is a pretty stable version of the HTML language. HTML 4.01 was also used to make the World Wide Web. This version is the official standard at the moment, and it has better support for stylesheets (CSS) and better scripting for a wide range of multimedia features.
HTML5: This is the name for the most recent version of the HyperText Markup Language. It is also just called HTML5. In January 2008, the first draft of this edition was shown to the public. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and the Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group (WHATWG) are both important groups that are working on the HTML 5 version, which is still being improved.
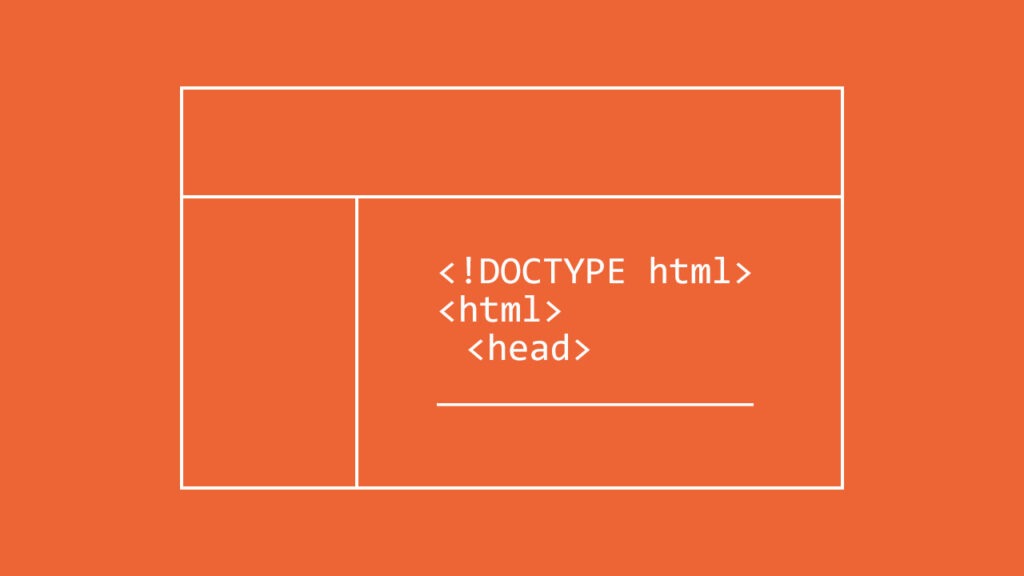
An Example Of HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My first heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanations
<!DOCTYPE>: This is a command that tells the browser what version of HTML is being used or what kind of document is being shown.
<html>: This tag tells the browser that the file being looked at is an HTML file. The text that is between the html tags describes the web document. With the exception of the <!DOCTYPE> tag, it holds all of the other HTML elements.
<head>: It should be the first element inside the html element, and it should hold the metadata. The full name of the head element is “head” (information about the document). Before the body tag can be opened, it has to be closed.
<title>: The title of an HTML page, which is shown at the top of the viewer’s window, is what the title> tag is for, and it does exactly what its name says. It needs to be put inside the head tag, and as soon as it’s there, it needs to snap shut.
<body>: The text inside the body element is used to explain to the end user what is in the main body of the page. This tag is where the HTML document’s main text content can be found.
<h1>: The text inside a h1 element is used to describe the first level heading of a webpage.
<p>: On a webpage, the text inside the p element is used to describe the paragraph.
Recommended reading: What Is Web Development? An Overview to Get Started
7 Main Differences Between HTML And HTML5
The biggest difference between HTML and HTML5 is that HTML5 now lets you use new types of form controls. HTML5 also added a number of semantic tags, like “article,” “header,” and “footer,” which describe the content in more detail.
1. Browsers
HTML works well in older browsers, while HTML5 works well in newer browsers and also supports older browsers. This is yet another way that HTML and HTML5 are different.
2. Type
Also, HTML is a language with less detail than HTML5, which is a language with more detail.
3. Vector Graphics
Another difference between HTML and HTML5 is that HTML5 can handle vector graphics, but HTML cannot. HTML can make vector graphics work with the help of other software or plugins. On the other hand, vector graphics are an important part of HTML5.
4. Multimedia
It is hard to add multimedia to HTML and hard to keep track of it once it is there. HTML5 makes it easy to add and manage multimedia content (such as audio and video, among other formats). Because of this, a big difference between HTML and HTML5 is the use of multimedia elements.
5. Help With Off-site Storage
Also, HTML and HTML5 are not the same because HTML doesn’t support offline storage. This is another difference between the two. HTML doesn’t have very good support for offline storage, unlike HTML5, which has great offline storage support.
6. Help With Web Sockets
Web sockets are not currently supported by HTML. On the other hand, HTML5 supports web sockets, which allow communication in both directions. The difference between HTML and HTML5 can also be seen in this way.
7. Geolocation
HTML doesn’t have geolocation, but HTML5 does.
The 7 Features Of HTML

1. Easy To Learn
It’s an easy language to learn and understand. It’s not hard to understand, and it’s simple to adapt to new situations.
2. Effective Presentation
Using this language to make a good presentation isn’t too hard because HTML comes with a lot of tags that can be used to change the way things look.
3. Flexibility
Since it’s a markup language, it gives you a flexible way to make web pages with text and images, which you can do along with the content. This can be done by putting the two things together.
4. Link Optimization
It makes it easy for programmers to add a link to a web page (using the html anchor tag), which makes the user want to look around the website more.
5. Platform-Independent
Because it can be shown on any platform, including Windows, Linux, and Macintosh, it is seen as independent of any platform.
6. Multimedia Elements
It makes it easier for the programmer to add multimedia elements to web pages, such as pictures, videos, and sounds. All of these things help make the website more interactive and appealing to look at.
7. Case-Insensitive
Since HTML is a language that doesn’t care about the case of its words, we can use either lowercase or uppercase components in our documents.
Recommended reading: What Is a Front End Developer and How to Become One?
How Does HTML Work?
HTML is like other programming languages in that it is made up of a series of commands and blocks of text that are then turned into what the user sees. This is done so that web browsers can understand HTML.
If you are using a desktop or laptop computer and want to see what the HTML code on this page looks like, you can do so by right-clicking anywhere on this page and choosing “View Page Source” from the context menu. This is the right way to get to the HTML code of a page (the option may vary depending on your browser). When you click on it, you should be taken to a big block of text that has code in it.
As we’ve already talked about, HTML can tell a browser where to get more resources and what to do with the content on a page by using a series of tags. Some of these instructions can tell the browser where to look for more things to load. Even though there are more than 100 HTML tags that can be used, most websites only need a small number of them to work as they should.
Top 5 HTML Practices
1. Make a list of all the pages with URLs that are clear and full of keywords
If you use HTML, you can change the URL of your pages by hand. Use this to your advantage by making websites that are easy to understand not only for people but also for search engines. Make sure that the words “swimming trunks” are in the URL of a page about swimming trunks, for example. This may seem like a no-brainer, but there are a lot of URLs out there that use letters, words, and other things that don’t mean anything and hurt the organic SEO of a page.
2. Use title tags that mean something
Using the title> tag, you can give a web page more meaning and make it easier for search engines to find. For example, the text inside the title> element is shown on the page that shows the results of a Google search, as well as on the user’s web browser bar and tabs.
3. Write unique content full of keywords
By using keywords and key phrases in the body text in a natural way, you not only send good signals to search engines but also let readers know they are in the right place. As a general rule, keywords should be used a few times throughout the content, sometimes making up 1% to 2% of the text on a page. To make search engine optimization better, keywords should be used. This means that between one and two of the 100 words on a page should be keywords.
4. Write consistent code
A code base that is neatly written and indented correctly shows that you are a professional and care about other people who may need to work on your code in the future. It’s a good idea to start your work with clear and correctly indented marks to make it easier to read.
5. Link to external and internal pages
You can show Google that a certain page is linked to the rest of your site by linking to other pages on your site that are about the same subject. It also gives readers the option of clicking through to other interesting parts of your website, which can make their reading experience much better. By using this search engine optimization (SEO) strategy, which shows search engines and readers that you know what other information people might be looking for on the web, you can increase the number of people who visit other pages on your website.
Recommended reading: How To Outsource SEO & Web Design Processes?
If you put external links in your content, both your readers and search engines will be able to tell that the information you provide comes from credible, authoritative, and trustworthy sources. Though you may pass link equity to them from your site, linking to external sources whose domains end in.gov or.edu is a great way to show that you only trust the most trustworthy organizations, which will make a reader more likely to trust you. Even if you pass link equity to them from your site, linking to outside sources whose domains end in.gov or.edu is a great way to show that they are trustworthy.
Recommended reading: Top 7 Web Development Languages To Use in 2022
The 5 Best HTML Editors
In order to build our first website, we need a reliable HTML editor. There are many choices out there on the market. Below is a list of carefully selected ones.
1. Notepad++
Programmers who code in HTML and other languages often choose Notepad ++. It is a very small tool that you can download and use to do the things you need to do to write clean code.
People who like to work with images will find that this choice is fantastic. In addition to all of its basic features, Notepad++ has a graphical user interface (GUI) that lets users communicate with the program by using pictures to show what to do.
2. Komodo Edit
One of the two editors that were published by the same label is called Komodo Edit. They provide a straightforward, open-source editor that is compatible with a wide number of add-ons and languages.
Like Notepad++, it’s free to download and an incredible editor in its own right.
3. Adobe Dreamweaver CC
Next on our list of the best HTML editors is Adobe Dreamweaver CC. This HTML editor is a great choice for you to think about if you are a coder looking for a program with a lot of coding features.
Adobe Dreamweaver CC is designed for professionals who want a tool that lets them customize and be creative while also making coding easy and effective.
4. Sublime Text 3
Users of Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux can use Sublime Text 3 because it works on all three platforms and is free. It can be changed in a lot of ways and is easy to use, which makes it a great choice for a wide range of users.
5. Atom
Atom is the last one on our list. Most people agree that Atom is one of the best HTML editors on the market. This open-source editor gives programmers access to high-quality tools at a low cost, so they can get what they need without putting a strain on their finances.
Atom is a great tool for building websites because it has a great mix of simple and advanced features. This makes it a great choice for both people who have never built a website before and those who have been doing it for years.
FURTHER READING: |
2. 12 Free HTML5 Resources To Learn for Newbies |
3. Web Application Development Tutorial: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners |
4. 23 Awesome Web Development Tutorials for Beginners |
So, What Is HTML?
Without hypertext markup language (HTML), the world wide web would not be what it is today. HTML is the language that is used to create the structure that makes up the World Wide Web. This structure includes page layouts, paragraphs, links, tags, and attributes. Whenever any of us browse the internet, HTML is almost certainly present, regardless of whether or not we are aware of its presence.
With the help of this article, Designveloper aims to be able to provide a comprehensive response to the question “What is HTML?” Please don’t hesitate to get in touch with us if you need expert consulting or services related to HTML.